.NET and Why You Should Care
What is .NET?
.NET is an open-source developer platform from Microsoft for building all sorts of applications.
What's a Developer Platform?
- A developer ecosystem
- A set of tools and libraries that accelerate the development of your applications
.NET Strikes a Balance Between
- Productivity
- Performance
- Security
- Reliability
Web
- ASP.NET
- Blazor (Server & WebAssembly)
Desktop
- Blazor Hybrid
- WinUI and WinAppSDK
- MAUI
Microservices and Cloud
- Serverless
- Designed for Docker
IoT (Internet of Things)
- IoT Libraries (including device bindings)
- Wilderness Labs Meadow Board
.NET Does All of This While Using the Same:
- Programming languages
- Libraries
- Tools and techniques
How Does .NET Do All of This?
Programming Languages
- Visual Basic
- F# (F Sharp)
- C# (C Sharp)
Tooling
- Base Class Library (BCL)
- Nuget (package management)
- Visual Studio (Windows & Mac)
- Command line tools -
dotnet
The Compiler
- Code Analysis
- Language Server
- Type Checking
- Refactoring/Formatting
- And of course, compiling
Common Intermediate Language (CIL)
| .assembly Hello {} |
| .assembly extern mscorlib {} |
| .method static void Main() |
| { |
| .entrypoint |
| .maxstack 1 |
| ldstr "Hello, world!" |
| call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string) |
| ret |
| } |
Common Language Runtime (CLR)
- The .NET virtual machine
- Just in time (JIT) compilation
- Memory management/garbage collection
- Type safety and exception handling
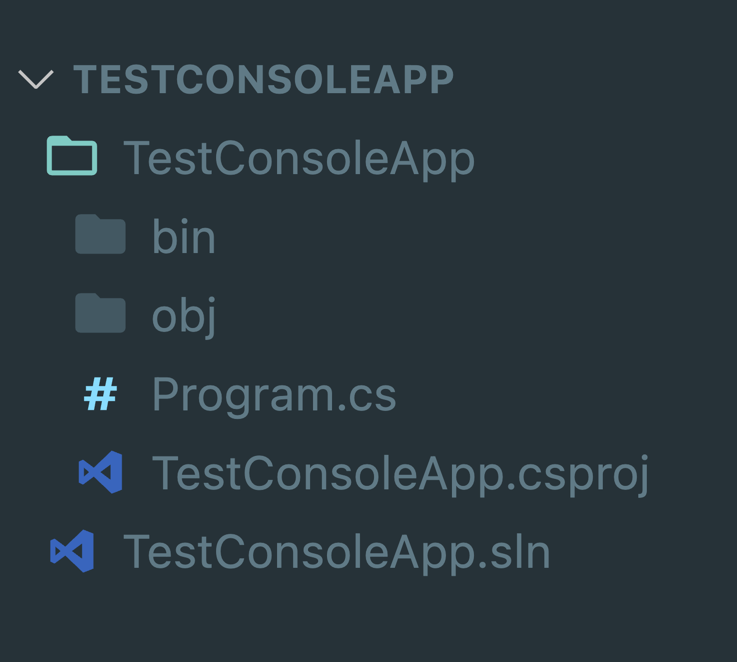
Anatomy of a .NET Project
Files and Layout
.csproj - Defines a C# project - Build configuration
- Dependencies
.sln - Organizes multiple projects (monorepo).cs - C# source fileobj - Object, or intermediate, filesbin - Binary files
Assemblies
- Unit of deployment and versioning
- Contains compiled code, resources, metadata
- Can be process assemblies (
.exe) or library assemblies (.dll) - Can have dependencies on other assemblies
- Loaded and executed by .NET runtime
A Note on .NET Versions
- .NET Framework
- .NET Core
- A unified .NET (.NET 5+)
C# Syntax
| using System; |
| |
| namespace MyNamespace; |
| |
| class Program { |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| string message = "Hello, world!" |
| |
| Console.WriteLine(message); |
| } |
| } |
| using System; |
| |
| namespace MyNamespace; |
| |
| class Program { |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| string message = "Hello, world!" |
| |
| Console.WriteLine(message); |
| } |
| } |
| using System; |
| |
| namespace MyNamespace; |
| |
| class Program { |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| string message = "Hello, world!" |
| |
| Console.WriteLine(message); |
| } |
| } |
| using System; |
| |
| namespace MyNamespace; |
| |
| class Program { |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| string message = "Hello, world!" |
| |
| Console.WriteLine(message); |
| } |
| } |
| using System; |
| |
| namespace MyNamespace; |
| |
| class Program { |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| string message = "Hello, world!" |
| |
| Console.WriteLine(message); |
| } |
| } |
C# Syntax - Control Flow
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| if (myInt > 10) { |
| |
| } else { |
| |
| } |
| |
| foreach (var item in myList) { |
| |
| } |
| |
| try { |
| |
| } catch (Exception ex) { |
| |
| } |
| } |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| if (myInt > 10) { |
| |
| } else { |
| |
| } |
| |
| foreach (var item in myList) { |
| |
| } |
| |
| try { |
| |
| } catch (Exception ex) { |
| |
| } |
| } |
| static void Main(string[] args) { |
| if (myInt > 10) { |
| |
| } else { |
| |
| } |
| |
| foreach (var item in myList) { |
| |
| } |
| |
| try { |
| |
| } catch (Exception ex) { |
| |
| } |
| } |
C# Syntax - Properties
| class Person |
| { |
| private int age; |
| public int Age { |
| get { return age; } |
| set { age = value; } |
| } |
| |
| public string FirstName { get; set; } |
| public string LastName { get; set; } |
| |
| public string FullName => $"{FirstName} {LastName}"; |
| } |
| class Person |
| { |
| private int age; |
| public int Age { |
| get { return age; } |
| set { age = value; } |
| } |
| |
| public string FirstName { get; set; } |
| public string LastName { get; set; } |
| |
| public string FullName => $"{FirstName} {LastName}"; |
| } |
| class Person |
| { |
| private int age; |
| public int Age { |
| get { return age; } |
| set { age = value; } |
| } |
| |
| public string FirstName { get; set; } |
| public string LastName { get; set; } |
| |
| public string FullName => $"{FirstName} {LastName}"; |
| } |
C# Syntax - Inheritance
| public class Animal { |
| public virtual void MakeSound() { |
| Console.WriteLine("The animal makes a sound"); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| public class Cat : Animal { |
| public override void MakeSound() { |
| Console.WriteLine("The cat meows"); |
| } |
| } |
| public class Animal { |
| public virtual void MakeSound() { |
| Console.WriteLine("The animal makes a sound"); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| public class Cat : Animal { |
| public override void MakeSound() { |
| Console.WriteLine("The cat meows"); |
| } |
| } |
| public class Animal { |
| public virtual void MakeSound() { |
| Console.WriteLine("The animal makes a sound"); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| public class Cat : Animal { |
| public override void MakeSound() { |
| Console.WriteLine("The cat meows"); |
| } |
| } |
C# Syntax - Attributes
| [Serializable] |
| public class MyClass { |
| [Obsolete("This method is deprecated.")] |
| public void MyOldMethod() { |
| |
| } |
| } |
| [Serializable] |
| public class MyClass { |
| [Obsolete("This method is deprecated.")] |
| public void MyOldMethod() { |
| |
| } |
| } |
C# Syntax - Generics
| public class MyGenericClass<T> { |
| private T[] myArray; |
| |
| public MyGenericClass(int size) { |
| myArray = new T[size]; |
| } |
| |
| public void SetItem(int index, T item) { |
| myArray[index] = item; |
| } |
| |
| public T GetItem(int index) { |
| return myArray[index]; |
| } |
| } |
| public class MyGenericClass<T> { |
| private T[] myArray; |
| |
| public MyGenericClass(int size) { |
| myArray = new T[size]; |
| } |
| |
| public void SetItem(int index, T item) { |
| myArray[index] = item; |
| } |
| |
| public T GetItem(int index) { |
| return myArray[index]; |
| } |
| } |
| public class MyGenericClass<T> { |
| private T[] myArray; |
| |
| public MyGenericClass(int size) { |
| myArray = new T[size]; |
| } |
| |
| public void SetItem(int index, T item) { |
| myArray[index] = item; |
| } |
| |
| public T GetItem(int index) { |
| return myArray[index]; |
| } |
| } |
| public class MyGenericClass<T> { |
| private T[] myArray; |
| |
| public MyGenericClass(int size) { |
| myArray = new T[size]; |
| } |
| |
| public void SetItem(int index, T item) { |
| myArray[index] = item; |
| } |
| |
| public T GetItem(int index) { |
| return myArray[index]; |
| } |
| } |
Productivity 🔨
- Cross platform
- Covers most application types
- Large BCL for reusable code
- Powerful debugging tools
Performance 🔥
- JIT compilation
- Native interoperability
- Multi-threading support
Security 🔒
- Regular updates
- Strong Cryptography
- Sandboxed execution environment
Reliability 🛡️
- Strong type system
- Automatic memory management
- Stable runtime
- Support from Microsoft